8 kidney function and location
Our body requires nutrients, vitamins, and minerals to do day to day physical and mental activities. The kidney function and location is mainly dependents on our stomach. Our stomach will break the food we eat or drink into chemical compounds (such as potassium and sodium) and make them available for further nutrition supply, such as providing oxygen, iron, and protein to blood. After processing these nutrients, it will throw out all unwanted wastes the body generates.
In discharging the waste products, our excretory system plays a significant role in getting rid of it and avoiding unwanted waste collections. The human body has several parts like Sweat Glands, the Liver, the Lungs, and the Kidney system, taking part in discharging the waste products.
Table of Contents
What are Kidneys?
Kidneys consist of three sections:
- an inner layer called the Medulla
- an outer layer called the Renal Cortex
- lastly, the Renal Pelvis, which transports the urine from the Kidney to the ureter.
These kidneys help pass our waste as urine and act as a natural filter of the blood before transferring it back to the heart.
During this filtration process, the body will produce Urea, water, and other chemical compounds.
The waste filtered by the kidneys gets removed through the output port called the urethra as urine; along with the above process, kidneys produce essential hormones, like Erythropoietin and Vitamin D. This hormone controls the Red Blood Cells production in the Bone Marrow. Similarly, kidneys balance the Acid-Base, regulates electrolytes, and conserve fluids.
The human excretory system consists of:
- Kidneys – 2
- Ureters – 2
- Urinary bladder – 1
- Urethra – 1
This post is about Kidney Function and Location; we will discuss it a bit deeper.
Why are Kidneys so Important?
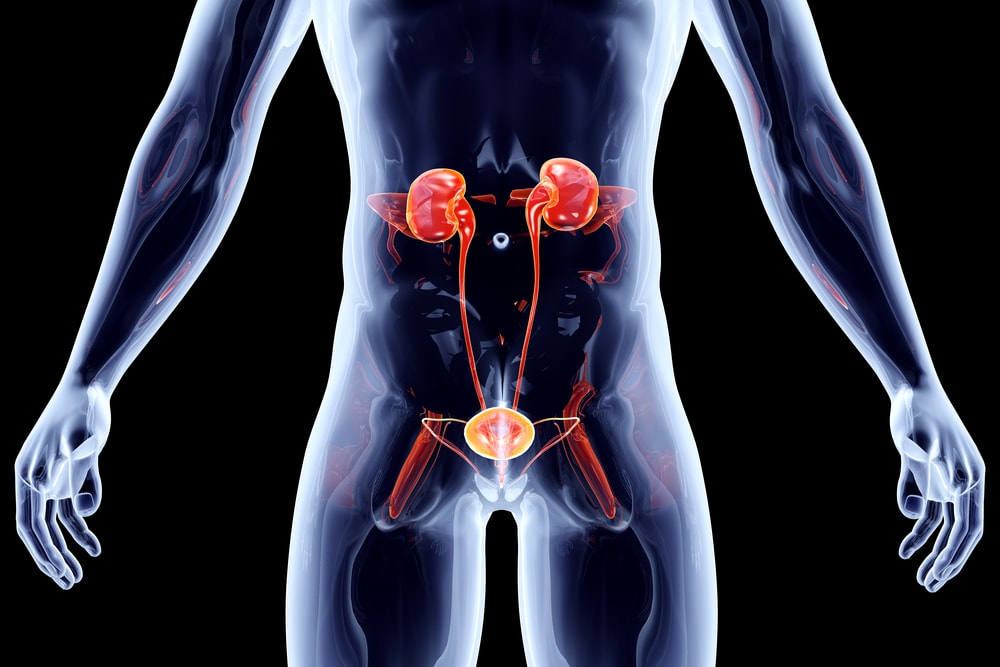
Our kidneys remove unwanted waste and toxins out of the blood (extra fluid) from our bodies. It also helps to remove acid produced by our body’s cells and maintains a healthy balance of water, salts, and minerals, such as sodium, calcium, phosphorus, and potassium in our blood.
In this process, the filtering unit, which is Nephron, plays an important role. At this stage, Remember, Nephrons are Just like millions of pores in our “Water Filter.” And all together, these bunch of Nephrons collectively forms the Kidneys Filtering system.
After filtering blood, unwanted waste and toxins come into Renal Pelvis (we will see in the coming paragraph) and made available to pass via Ureters and Bladder to the urethral opening.
Kidney Function and Location
- Locations of Kidneys
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs approximately 5-7 cm (1.97 – 2.76 inches) wide and 10-12 cm (3.93 – 4.72 inches) long, 2-3 cm (0.79 – 1.18 inches) in thickness. It weighs around 120 gm to 170 gm (4.23 to 5.997 ounces) in males and 120 gm to 135 gm (4.23 to 4.76 ounces) in females.
Internal Location in Human Body :
- Locates just below the Rib cage and Diaphragm,
- Between T12 and L3 of the Spinal Cord.
- T12 Protects our Kidneys
- It is also called Retroperitoneal Gland (Retro – Going Backward, Peritoneal – Peritoneal Cavity in the human body)
- The right side Kidney is slightly lower in position than the left Kidney due to the liver’s weight on the Right one.
Some Important attributes :
- Dark Red in color – Due to a Bunch of networks of blood capillaries.
- Slightly flattened
- Bean Shaped (bean – vegetables for human or animal food)
- Each kidney weighs about 160 grams(5.64 ounces) and filters between 1 and 1,5 liters(0,22 and 3.3 gallons) of urine daily. Approx. 150 – 200 Liters(32.9954 – 43.9938 gallons) of blood are collectively filtered daily by both kidneys.
- Adrenal Gland – On top of each Kidney.
Structure Of the Kidneys
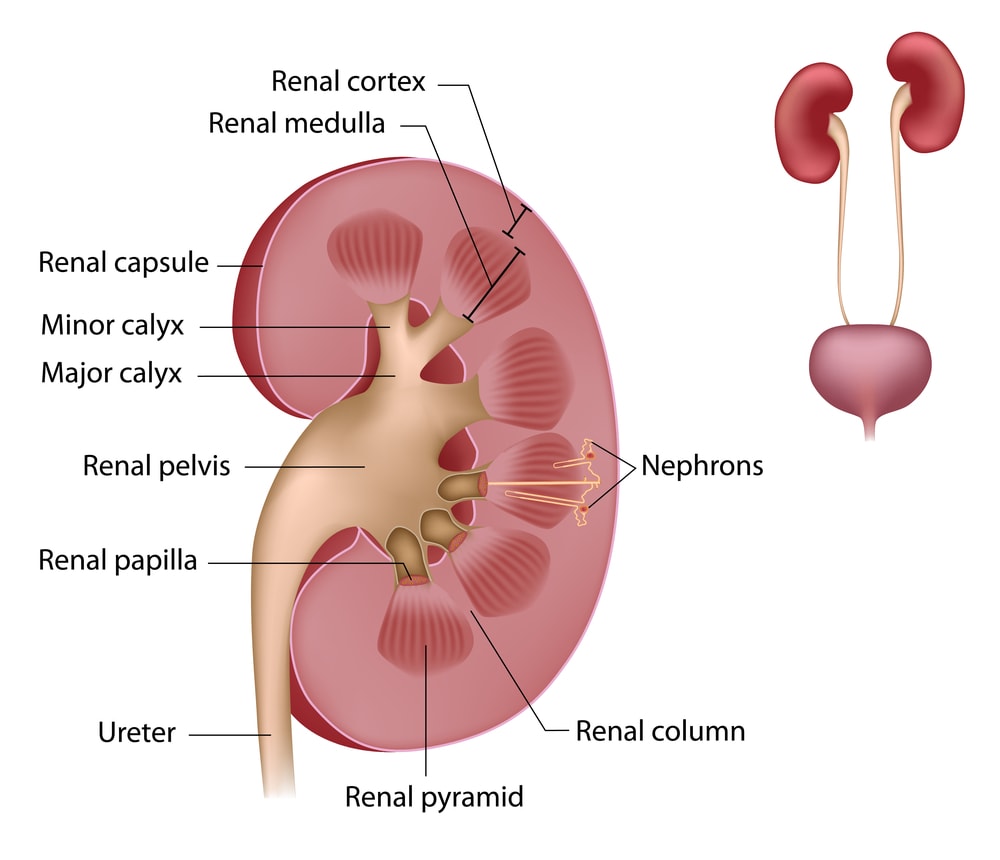
Renal Corpuscle – Its location is in the renal Cortex and comprises a wide array of capillaries. They are known as the glomerulus and the capsule; it is a cup-shaped chamber that surrounds it and is called the glomerular or Bowman’s pill.
Renal Pyramid – Its structure looks like a cone shape known as kidney tissue called Malpighian pyramids, named after Marcello Malpighi, a seventeenth-century anatomist.
Renal Cortex – It is an outer part of the kidney structure and contains the glomerulus and convoluted tubules. It plays a vital role in ultra filtration urine formation—renal Cortex surrounded by a renal capsule, a fatty tissue layer.
Renal Medulla – It contains a cluster of nephrons and also acts as an inner tissue of the Kidney. It consists of Renal Pyramid and collecting ducts.
Renal Pelvis – The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped space located in the part of the Kidney acts as a pathway for fluid on its way to the bladder through ureters. It consists of Calyces and Hilum.
Nephrons
Nephrons are basic functional units of Blood filtration and Urine production. Each Kidney contains around 1 million to 1.5 million nephrons.
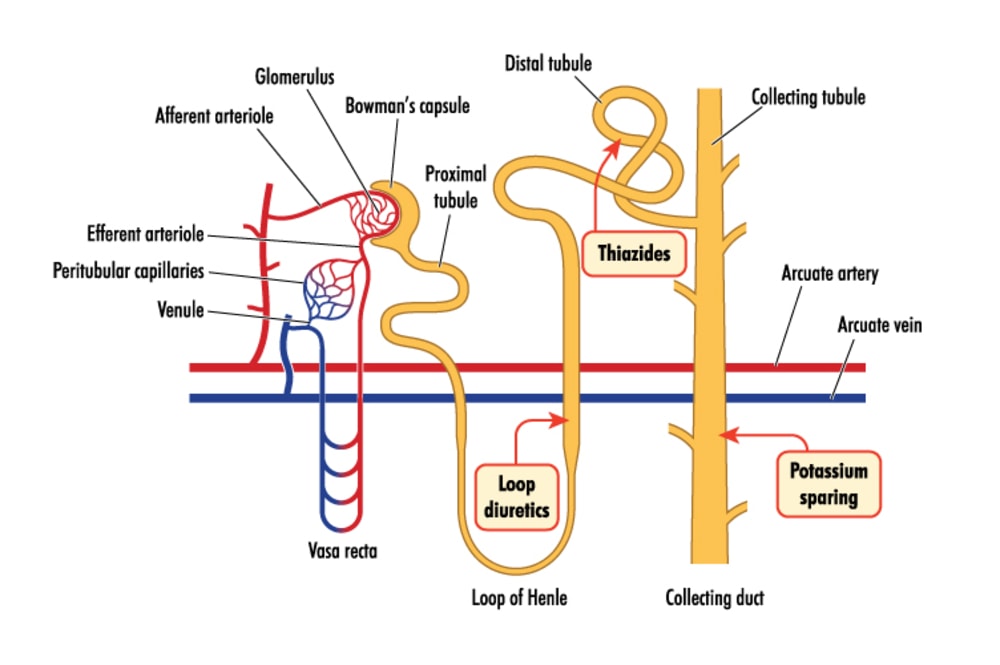
Nephrons are a long tube-like structure, and its length varies from 35–55 mm (1.38 – 2.17 inches) long.
Nearly One million Nephrons are present in One Kidney, and in the total count, the human body comprises around 2 – 2.5 million nephrons.
The structure of the Nephron divided into two parts:
- Renal Tubule
- Renal Corpuscle
Types of Nephron
- Cortical Nephron – It is present within the Cortex, short in length, and comprises about 80% of the total nephrons.
- Juxtamedullary Nephron – These are long loops of Henle and extended into the Medulla and contains about 20% of remaining nephrons.
Functions of the Kidneys
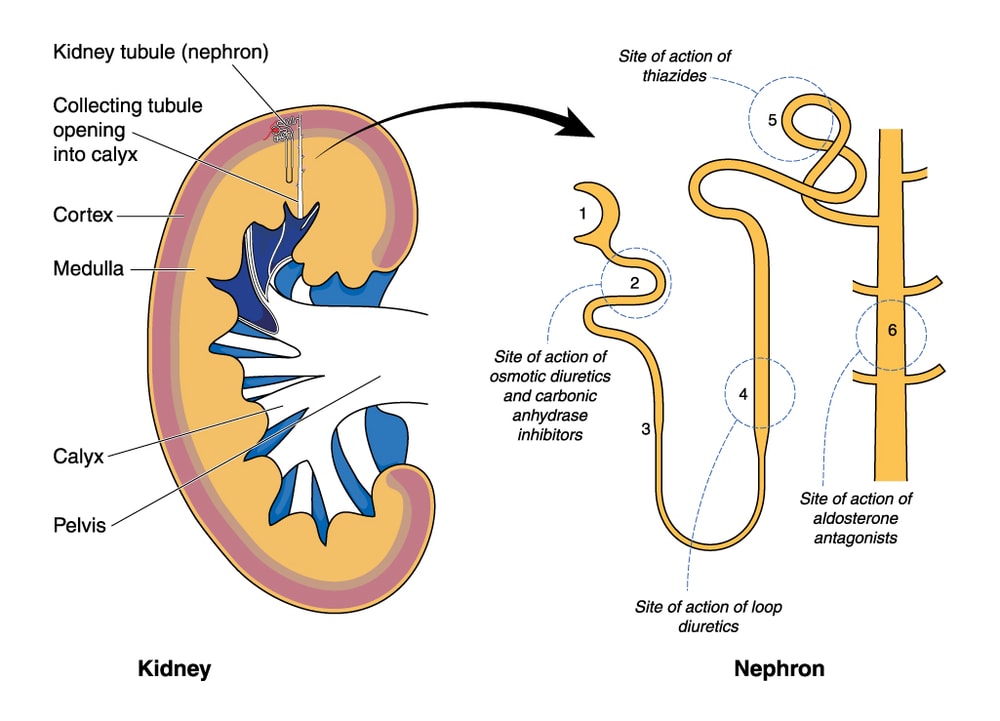
The most known standard function of kidneys are as follows,
- Removing waste and toxic by-products
- Extract toxins from the body,
- Adjust the body’s fluids, and control red blood cell production.
- Maintains the blood’s chemical balance and regulates our body’s sodium, potassium, and calcium level.
- Production of vitamin D, which keeps our bones strong, healthy.
Some Important Hormones produced by kidneys
Renal functions as filtering unite for our body, especially for Blood filtering:
- It obtains the balance of Acid-Base for needy fluids
- regulates hormones of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), Erythropoietin (EPO), and 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3.
Erythropoietin (EPO) is very important to maintain healthy oxygen levels in our tissues.
Also, Renin is an enzyme produced by the kidneys. It plays a superman role in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone hormonal system, which helps to control our blood pressure.
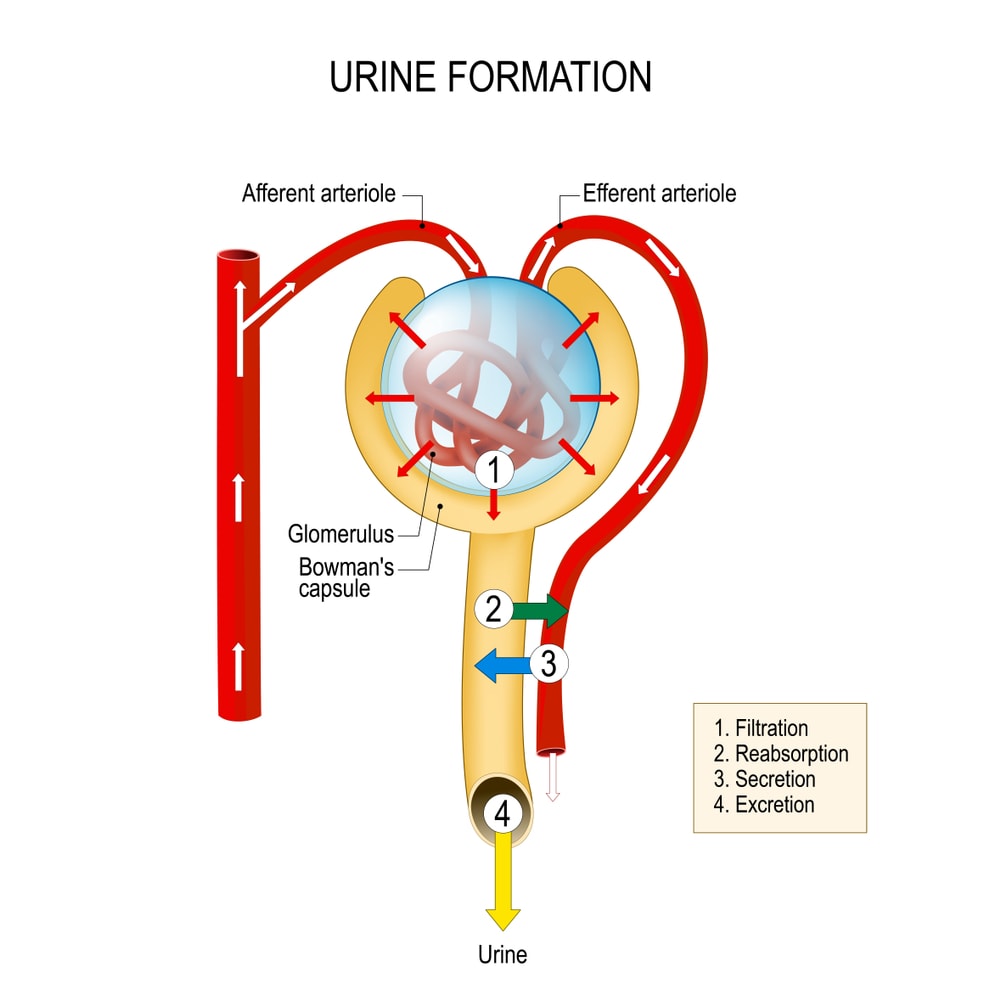
The function of Nephrons – A nephron consists of a filtering unit of tiny blood vessels known as glomerulus attached to a tubule. When blood enters the glomerulus, it gets filtered, and the separated fluid or toxic waste then passes through the tubule.
In the tubule, chemical substances and water are either added to or removed from this filtered fluid as per our body’s needs, the final product being the urine we excrete through the urethra.
Renal Medulla function – The primary function of the Medulla is to control the concentration of the urine, which flows from the collecting ducts to the renal pelvis. The process is subjected to one direction, only peristaltic movements, to enable drainage of the urine the downstream of ureter and bladder.
Renal Cortex function – It is an essential part of the kidneys, where the ultra filtration of blood is happening here, and at the same time, producing Erythropoietin too.
The renal Pelvis functions – as a funnel cavity for collecting the urine produced in the Kidney and passes it to a central “stem,” known as the ureter.
Renal Artery Function – It supplies the oxygenated blood to our kidneys
Renal Vein Function – Once kidneys have filtered the blood, it is sent back through this renal vein to the heart’s right side section’s inferior vena cava.
How do your kidneys work?
Each of our kidneys consists of about a million’s filtering units called Nephrons. Each Nephron is a microscopic structural, and functional unite of our Kidneys and works as a filter (Just like our water filter’s small filter pores). It consists of Glomerulus and Tubule.
The nephrons work through a two-step process:
- The Glomerulus filtration – filters your blood, and
- The Tubule reabsorption – Sends back needed substances to our blood and removes wastes.
After every food consumption or drink, our stomach process it and breaks it into chemical compounds.
Chemical compounds happen, so that essential nutrient gets absorbed by individual cells and tissues and ultimately combines with our blood.
Our blood flows through the heart as De-oxygenated and Oxygenated Blood via Veins and Arteries, respectively. Oxygenated blood further goes to the kidneys to get purified and filtered.
In this stage, around 5-6 liter (1.32086 – 1.58503 gallons) of blood flows through the kidneys filtering system and gives back filtered or pure blood to the heart, and this blood will be in less amount compared to entered blood.
After filtration of blood, some unwanted wastes and toxic liquid form fluids get separated and made available to throw out of our body via Ureters as urine.
Types of Kidney Problems & Causes
Due to unhealthy diet, dehydration, excessive saturation of acidic and toxic compounds in urine may lead to various kidney problems. It may be Chronic Kidney disease or Kidney Stone or Acute Kidney or urinary infections.
What is Kidney Disease?
The abnormalities in blood filtration or pain in the Kidney indicate some point of Kidney Disease. It affects kidneys’ main functionalities, and if you ignore it for a long time, it can lead to a series of issues.
It can also affect the production of red blood cells and vitamin D needed for metabolism and healthy bones.
Sign & Symptoms of Kidney Disease
Sign & Symptoms are non-specific; it might be corresponding to other diseases symptoms also. But dehydration causes pain in kidney areas, stomach or back pain may be signal kidney problems. You’ll experience:
- Sleep issues
- Vomiting & Nausea
- Muscle twitches and cramps
- Shortness of breath, more especially if fluid builds up in the lungs (Also you may get exposure to COVID-19)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
Causes of Kidney Disease
- Hypertension
- High Blood Pressure
- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- Recurrent kidney infection is also called pyelonephritis and Ignoring over several months or years.
- Lengthen blockage of the urinary tract from issues such as:
- Swollen prostate
- Kidney stones
- Some cancers
Chronic kidney disease
The Dangerous level of toxic substances, fluids, electrolytes, or wastes concentrates in a particular area of the Kidney, and then it is considered chronic kidney disease. This disease leads to a progressive loss of kidney functioning.
At the starting stage, you don’t feel much pain or any symptoms but, after some time, suddenly wake you up by giving lots of pain and a series of kidney problems.
Kidney stones
These are Hard Stone or pebble-like materials made up of a high concentration of certain minerals and chemicals formed from substances in the urine, such as Calcium Oxalate or Phosphate, Uric Acid, or Cystine Stones.
To understand a broader aspect of kidney disease, here are other articles where we explore other kidney-related issues:
- If you want to know what is kidney stone pain like, Click here.
- For reasons on why do my kidneys hurt at night, Click here.
- What Does The Pancreas Do In Your Body? Click here.
- Kidneys Location, Structure, and Function, Click here.
Please take a look and come back to read more about kidney function and location.
Sign & Symptoms of Kidney stones
- Back pain or ache
- Not able to Urinate properly
- Foul-smelling or cloudy urination
- Blood in the Urine
- Vomiting & Nausea
- Fever & Feeling Cold (especially in summer)
Causes of Kidney stones
- 75% reason is dehydration, and others are as follows
- Excessive Body Weight
- An improper diet of Protein consumption
- Too much intake of :
- Salty products
- Sodium products
- Sugar products
- Too much food habit of animal proteins like:
- Beef
- Fish
- Pork
- Eggs
- Too much Soft Drinks, i.e., Carbonated Drinks like Sodas, etc
Polycystic kidney disease
It is an inherited disorder that consists of clusters of cysts developed in your Kidney. It may cause to expand in other parts of the body also. It can grow from small to very large and can damage your kidneys too.
Symptoms of Polycystic kidney disease
- Blood in Urine
- Intense Back pain comes and goes frequently.
- Headaches
- High Blood Pressure
- Urinary Tract Infections.
Cause of Polycystic kidney disease
- In most cases, Abnormal genes.
- Growth of cysts in the liver
- Loss of kidney function
- Development of an aneurysm in the brain
- Heart valve abnormalities
- Complications in Pregnancy
Acute kidney injury
It is widely known as sudden kidney failure within a few hours or days—the main reason for failing the right balance between fluids in our body after filtering the blood.
Symptoms of kidney injury
- Swelling around Ankles, Legs, and Eyes
- Fatigue & Tiredness
- Confusion
- Too little urine at the time of pee
- Chest pain
- Shortness of Breathing
Causes of kidney injury
According to doctors, acute renal failure and/or acute kidney injury are when your kidneys suddenly stop working. The leading causes are:
- Not enough blood flow to the kidneys
- Direct damage to the kidneys
- Urine backed up in the kidneys, especially in “sepsis.”
- A type of cancer called “multiple myeloma.”
- Blood or fluid loss
- Major surgery or Injuries
- An allergic response to some kinds of drugs (called “interstitial nephritis”)
Kidney infection
It is a particular type of urinary tract infection (UTI), which travels from the Urethral opening to the bladder to the ureters and reaches both or one of the Kidneys. It may damage our kidneys permanently if timely basis prompt medication and attention if not appropriately treated. The Doctors may prescribe you some antibiotics or may ask you to get hospitalized.
Symptoms of the kidney infection
- Frequent urination
- Burning sensation or pain while urinating or pee
- Pus or blood in your urine
- Abdominal or Back pain
- Fever & Cold feeling
Causes of the kidney infection
- Urinary tract blockage
- Weakened immune system
- Damage to nerves around the bladder
Precautions on how to Avoid Kidney Problems
- Get proper nutritious foods and avoid salty foods.
- Do regular 30 min exercise.
- Should have an empty stomach at least for 24 hours, once in a week, i.e., fasting
- Drink Juice and healthy fluids
- Don’t Smoke or consume Tobacco or Tobacco products.
- Do Yoga, Pranayam
- Regulate Blood Pressure Naturally
- Try to avoid unnecessary and too many medicines.
- Follow the Doctor, prescribed procedural medications.
- Use of Natural and Organic foods and avoiding preserved food products.
- Try to Avoid Animal Proteins
- Drink lukewarm water as much as you can daily.
FAQ’s
What are the primary functions of the kidneys?
It is the filtration of:
- Oxygenated blood
- Controlling Hormones
- Vitamin D
- Production Red blood cells.
Afterward, supplying back pure filtered blood to the heart and producing unwanted urine, which would be flowing through the ureter.
How do I improve my kidney function?
By following the precautions mentioned above. Such as,
- Do exercise
- Drink as much as water, pure and if possible lukewarm water is the best
- Eat fruits and try to avoid salty and animal protein food products
- Stay away from smoking, alcohol, if you can.
- Take enough sleep.
- Don’t keep or hold urinating for a long time.
What happens if your kidneys are not working correctly?
- You may feel like swelling; your palms or legs get swelling.
- You get thirsty, and your body asks you for more water for every minute.
- Feels like tired, or you may do vomiting and suddenly gets a fever or feeling chilled. Similarly, headache, abdominal pain, or flank pain may starts. To avoid this, please reach nearby doctors or any specialist to get proper medication.
What foods help repair kidneys?
- Onions
- Garlic
- Cauliflower
- Cranberries
- Cabbage
- Beans
What fruit is good for kidneys?
- Apple
- Coconut water
- Citrus Fruits like Orange, Watermelon
- Blueberries