Osteoporosis and Celiac Disease: Causes and Management

Osteoporosis and celiac disease are two separate medical conditions that can have a significant impact on a person’s overall health. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, making them more prone to fractures. Celiac disease, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system reacts negatively to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. While these two conditions may seem unrelated, there is a strong link between them that should not be overlooked.
Understanding the link between osteoporosis and celiac disease is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. By recognizing this connection, healthcare providers can better diagnose and treat patients who may be at risk for both conditions. For individuals with celiac disease, understanding the potential impact on bone health can help them make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle to minimize the risk of developing osteoporosis.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures.
- Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that damages the small intestine and affects the absorption of nutrients, including calcium.
- There is a link between osteoporosis and celiac disease, as people with celiac disease are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis.
- Celiac disease affects calcium absorption, which can lead to bone loss and osteoporosis.
- Diagnosis and screening for osteoporosis and celiac disease are important for early detection and management.
Understanding Osteoporosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Risk Factors
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by low bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to an increased risk of fractures. It occurs when the body loses too much bone or fails to make enough new bone. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of osteoporosis, including age, gender, family history, hormonal changes (such as menopause), certain medical conditions (such as rheumatoid arthritis), and lifestyle choices (such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption).
The symptoms of osteoporosis may not be noticeable until a fracture occurs. Common signs include back pain, loss of height over time, stooped posture, and easily fractured bones. Complications of osteoporosis can be severe and life-altering, including fractures that can lead to chronic pain, disability, and reduced quality of life.
Celiac Disease: What It Is and How It Affects Bone Health
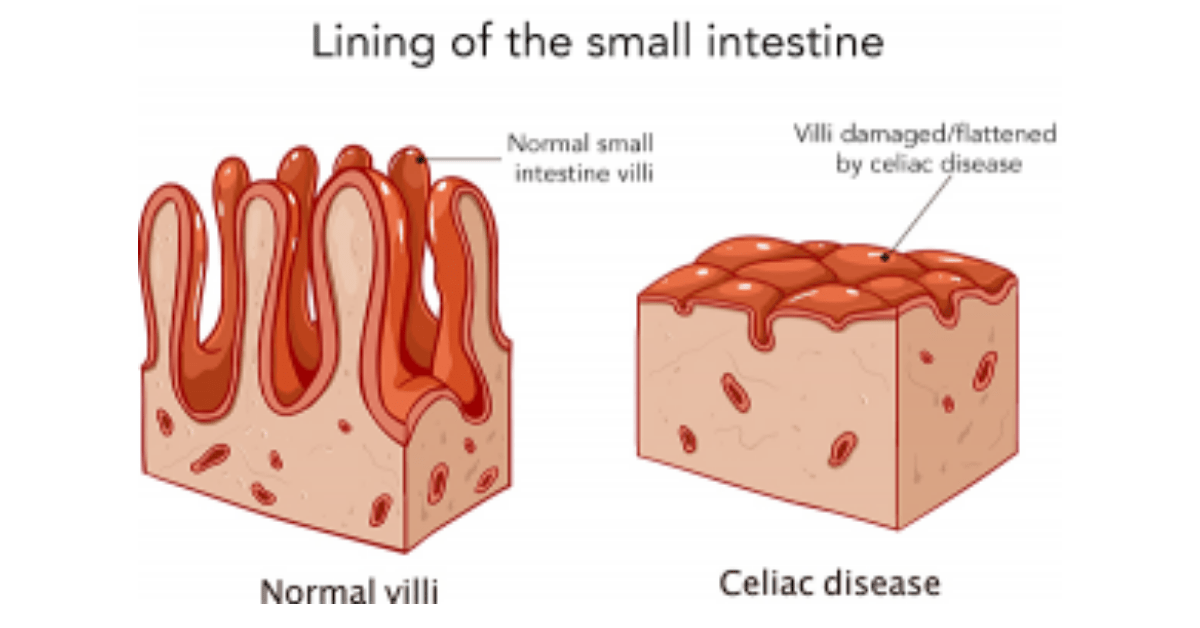
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system reacts negatively to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When someone with celiac disease consumes gluten, their immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine, causing damage and interfering with the absorption of nutrients from food. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms and complications, including malnutrition and deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
One of the key ways celiac disease affects bone health is through malabsorption of calcium. Calcium is a vital nutrient for bone health, and when the body is unable to absorb it properly, it can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of osteoporosis. Additionally, celiac disease can cause inflammation in the body, which can further contribute to bone loss.
The Link Between Osteoporosis and Celiac Disease
The link between osteoporosis and celiac disease lies in the fact that individuals with celiac disease are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis compared to the general population. Research has shown that individuals with celiac disease have a higher prevalence of osteoporosis and low bone density compared to those without the condition.
There are several reasons why celiac disease increases the risk of osteoporosis. First, as mentioned earlier, malabsorption of calcium due to damage to the small intestine can lead to calcium deficiency, which is essential for maintaining strong bones. Second, inflammation caused by celiac disease can contribute to bone loss. Lastly, individuals with celiac disease often have other risk factors for osteoporosis, such as vitamin D deficiency and hormonal imbalances.
Studies have shown that individuals with celiac disease are up to four times more likely to develop osteoporosis compared to those without the condition. It is important for healthcare providers to be aware of this link and screen individuals with celiac disease for osteoporosis to ensure early detection and appropriate treatment.
Gluten and Bone Health: How Celiac Disease Affects Calcium Absorption
Gluten, the protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, plays a significant role in the development of osteoporosis in individuals with celiac disease. When someone with celiac disease consumes gluten, it triggers an immune response that damages the lining of the small intestine. This damage interferes with the absorption of nutrients, including calcium.
Calcium is essential for bone health, as it helps build and maintain strong bones. When the body is unable to absorb calcium properly, it can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of osteoporosis. This is why individuals with celiac disease are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis compared to the general population.
It is important for individuals with celiac disease to follow a strict gluten-free diet to minimize the risk of bone loss and other complications associated with the condition. By eliminating gluten from their diet, they can reduce inflammation in the body and improve their ability to absorb calcium and other essential nutrients.
Diagnosis and Screening for Osteoporosis and Celiac Disease

Diagnosing osteoporosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Medical history includes assessing risk factors such as age, gender, family history, and lifestyle choices. Physical examination may involve assessing height loss, posture, and signs of fractures. Diagnostic tests such as bone density scans (DEXA scans) can measure bone density and determine if osteoporosis is present.
Celiac disease can be diagnosed through blood tests that measure specific antibodies related to gluten intolerance. If these tests are positive, a biopsy of the small intestine may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. It is important for individuals with celiac disease to be screened for osteoporosis due to the increased risk associated with the condition.
Early detection of both osteoporosis and celiac disease is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. Healthcare providers should be proactive in screening individuals at risk and providing appropriate treatment and lifestyle recommendations.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Osteoporosis and Celiac Disease
Lifestyle changes play a significant role in managing both osteoporosis and celiac disease. For individuals with celiac disease, the most important change is adopting a strict gluten-free diet. This involves avoiding all foods that contain gluten, including wheat, barley, rye, and any products made from these grains. It is also important to read food labels carefully, as gluten can be found in unexpected places such as sauces, dressings, and processed foods.
In addition to a gluten-free diet, individuals with osteoporosis and celiac disease should also focus on other lifestyle changes that promote bone health. Regular exercise, especially weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, and strength training, can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist to develop an exercise program that is safe and effective.
Medications for Osteoporosis: Benefits and Risks
There are several medications available for the treatment of osteoporosis. These medications work by either slowing down bone loss or increasing bone formation. Some common medications include bisphosphonates, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and denosumab.
Bisphosphonates are the most commonly prescribed medications for osteoporosis. They work by inhibiting the cells that break down bone, thus slowing down bone loss. SERMs mimic the effects of estrogen in the body and can help prevent bone loss. HRT involves taking estrogen and progesterone to replace hormones that are lost during menopause. Denosumab is an injectable medication that inhibits the cells that break down bone.
While these medications can be effective in treating osteoporosis, they also come with potential risks and side effects. It is important for individuals to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan based on their individual needs and risk factors.
Nutritional Management of Osteoporosis and Celiac Disease
Proper nutrition is essential for managing both osteoporosis and celiac disease. For individuals with celiac disease, following a strict gluten-free diet is crucial to prevent further damage to the small intestine and improve nutrient absorption. This involves avoiding all foods that contain gluten and focusing on naturally gluten-free foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and gluten-free grains like quinoa and rice.
In addition to a gluten-free diet, individuals with osteoporosis should also focus on consuming foods that are rich in calcium and other bone-healthy nutrients. Some examples include dairy products, leafy green vegetables, fortified plant-based milks, and calcium-rich seafood like sardines and salmon. It may also be necessary to supplement with calcium and vitamin D if dietary intake is insufficient.
Exercise and Physical Therapy for Osteoporosis and Celiac Disease
Exercise plays a crucial role in managing both osteoporosis and celiac disease. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, dancing, and strength training, can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures. These exercises put stress on the bones, which stimulates them to become stronger.
Physical therapy can also be beneficial for individuals with osteoporosis and celiac disease. A physical therapist can develop an exercise program tailored to an individual’s specific needs and limitations. They can also provide guidance on proper body mechanics and techniques to prevent falls and fractures.
Preventing Complications of Osteoporosis and Celiac Disease: Fractures and Malnutrition
Preventing complications of osteoporosis and celiac disease is crucial for maintaining overall health and quality of life. For individuals with osteoporosis, preventing fractures is a top priority. This can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and fall prevention strategies. Fall prevention strategies may include removing hazards in the home, using assistive devices such as handrails and grab bars, and wearing appropriate footwear.
For individuals with celiac disease, preventing malnutrition is essential. Following a strict gluten-free diet is the first step in ensuring proper nutrient absorption. It may also be necessary to supplement with vitamins and minerals, such as calcium and vitamin D, to address any deficiencies. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider can help identify any nutritional deficiencies and guide appropriate supplementation.
In conclusion, there is a strong link between osteoporosis and celiac disease that should not be overlooked. Individuals with celiac disease are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis due to factors such as malabsorption of calcium and inflammation. It is important for healthcare providers to screen individuals with celiac disease for osteoporosis and provide appropriate treatment and lifestyle recommendations.
Managing both osteoporosis and celiac disease requires a combination of lifestyle changes, including following a strict gluten-free diet, engaging in regular exercise, and taking appropriate medications and supplements. Early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing complications and maintaining overall health.
It is important for individuals with osteoporosis and celiac disease to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and risk factors. By taking proactive steps to manage both conditions effectively, individuals can minimize the impact on their bone health and overall well-being.
If you’re interested in learning more about the role of vitamins in our overall health, you may find this article on the function of Vitamin B in our life informative. Vitamin B plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and can be particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions such as osteoporosis and celiac disease. To understand how Vitamin B contributes to these conditions and its management, check out this article.
FAQs
What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a medical condition in which bones become weak and brittle, making them more prone to fractures.
What is celiac disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system reacts to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. This reaction damages the lining of the small intestine and can lead to malabsorption of nutrients.
What is the link between osteoporosis and celiac disease?
People with celiac disease are at an increased risk of developing osteoporosis due to malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D, which are essential for bone health.
What are the symptoms of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis often has no symptoms until a bone fracture occurs. However, some people may experience back pain, loss of height, and a stooped posture.
How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
Osteoporosis is diagnosed through a bone density test, which measures the amount of bone mineral in a specific area of the body, usually the hip or spine.
How is celiac disease diagnosed?
Celiac disease is diagnosed through blood tests that measure levels of certain antibodies, as well as a biopsy of the small intestine to look for damage to the lining.
What are the treatment options for osteoporosis?
Treatment options for osteoporosis include medications to increase bone density, calcium and vitamin D supplements, and lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and a healthy diet.
What are the treatment options for celiac disease?
The only treatment for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet, which involves avoiding all foods and products that contain gluten. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms.