Celiac Disease Treatment Options: Medications and Lifestyle

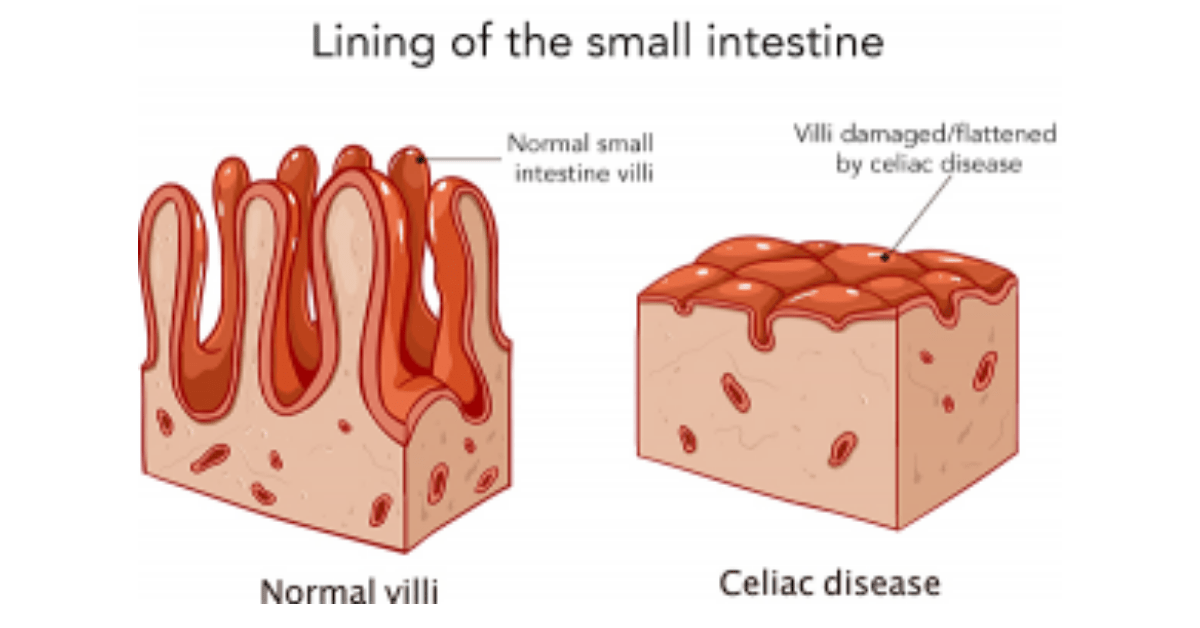
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine and is triggered by the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When individuals with celiac disease consume gluten, their immune system responds by attacking the lining of the small intestine, leading to inflammation and damage. This can result in a wide range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, and weight loss.
Early diagnosis and treatment of celiac disease are crucial to prevent further complications and improve quality of life. If left untreated, celiac disease can lead to malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, and an increased risk of certain types of cancer. Therefore, it is important for individuals experiencing symptoms to seek medical attention and undergo testing for celiac disease.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Celiac disease can be managed through a combination of medication, diet, supplements, and lifestyle changes.
- Gluten-free diet is the primary treatment for celiac disease, but it may not be enough for some patients.
- Nutritional supplements can help address nutrient deficiencies caused by celiac disease.
- Alternative therapies such as acupuncture and probiotics may provide additional benefits for celiac disease patients.
- Regular medical checkups and psychological support are important for managing celiac disease and improving quality of life.
Medications for Celiac Disease Treatment
While there is currently no cure for celiac disease, medications can be used to manage symptoms and reduce inflammation in the small intestine. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system’s response to gluten. Immunosuppressants, such as azathioprine or methotrexate, may also be used to control the immune response.
However, it is important to note that medication treatment for celiac disease is not without its drawbacks. Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants can have significant side effects and may not be suitable for long-term use. Additionally, these medications do not address the underlying cause of celiac disease – the immune system’s reaction to gluten – and therefore do not provide a permanent solution.
Gluten-Free Diet as a Primary Treatment for Celiac Disease
The most effective treatment for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet. This means completely avoiding all foods and products that contain gluten. Following a gluten-free diet allows the small intestine to heal and reduces inflammation, leading to a reduction in symptoms and an improvement in overall health.
A gluten-free diet involves avoiding foods such as bread, pasta, cereals, and baked goods that contain wheat, barley, or rye. It is important to read food labels carefully, as gluten can be found in unexpected places, such as sauces, dressings, and processed foods. Instead, individuals with celiac disease can opt for gluten-free alternatives made from grains such as rice, corn, quinoa, and oats (as long as they are certified gluten-free).
Following a gluten-free diet can be challenging at first, but with time and practice, it becomes easier. It is important to educate oneself about safe and unsafe ingredients and to learn how to read food labels effectively. There are also many resources available, such as support groups and online communities, where individuals with celiac disease can find tips and advice on following a gluten-free diet.
Importance of Nutritional Supplements in Celiac Disease Treatment
Celiac disease can lead to nutrient deficiencies due to the damage caused to the small intestine. The small intestine is responsible for absorbing nutrients from food, so when it is inflamed and damaged, the body may not be able to absorb essential vitamins and minerals properly.
Common nutrient deficiencies in individuals with celiac disease include iron, calcium, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and folate. These deficiencies can lead to anemia, osteoporosis, and other health problems. Therefore, it is important for individuals with celiac disease to take nutritional supplements to address these deficiencies.
Supplements such as iron, calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins may be recommended by healthcare providers to ensure that individuals with celiac disease are getting the necessary nutrients. It is important to work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate dosage and type of supplements needed.
Alternative Therapies for Celiac Disease Treatment
In addition to medication and a gluten-free diet, some individuals with celiac disease may explore alternative therapies to manage their symptoms. These therapies include acupuncture, herbal remedies, and probiotics.
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Some individuals with celiac disease have reported improvements in their symptoms after undergoing acupuncture treatments. However, more research is needed to determine the effectiveness of acupuncture for celiac disease.
Herbal remedies, such as chamomile or peppermint tea, may also be used to soothe digestive symptoms associated with celiac disease. These remedies are generally safe but should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore the balance of gut flora and improve digestion. Some studies have shown that certain strains of probiotics may be helpful in managing symptoms of celiac disease. However, more research is needed to determine the specific strains and dosages that are most effective.
It is important to note that alternative therapies should not replace conventional medical treatment for celiac disease. They should be used as complementary therapies alongside a gluten-free diet and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Celiac Disease Symptoms

In addition to medication, diet, and alternative therapies, there are several lifestyle changes that can help individuals with celiac disease manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation. Stress has been shown to worsen symptoms in individuals with celiac disease, so finding ways to manage stress is important.
Regular exercise can also be beneficial for individuals with celiac disease. Exercise helps improve digestion, reduce inflammation, and boost mood. It is important to choose activities that are enjoyable and suitable for individual fitness levels.
Getting enough sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being. Lack of sleep can worsen symptoms and weaken the immune system. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a relaxing sleep environment can help improve sleep quality.
Importance of Regular Medical Checkups for Celiac Disease Patients
Regular medical checkups are essential for individuals with celiac disease to monitor their condition and detect any potential complications. It is recommended that individuals with celiac disease have regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider, usually every six months to a year.
During these checkups, healthcare providers may perform blood tests to monitor nutrient levels and check for any signs of inflammation or damage to the small intestine. They may also provide guidance on managing symptoms, adjusting medications or supplements, and addressing any concerns or questions.
In addition to regular checkups, individuals with celiac disease should seek medical attention if they experience any new or worsening symptoms, such as severe abdominal pain, persistent diarrhea, unexplained weight loss, or signs of malnutrition.
Psychological Support for Coping with Celiac Disease
Celiac disease can have a significant impact on an individual’s emotional well-being. The diagnosis of a chronic illness and the need to follow a strict diet can be overwhelming and lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and anxiety.
It is important for individuals with celiac disease to seek psychological support to help cope with these challenges. This can be done through individual therapy, support groups, or online communities where individuals can connect with others who are going through similar experiences.
Psychological support can provide individuals with celiac disease with a safe space to express their feelings, learn coping strategies, and gain support from others who understand their struggles. It can also help individuals develop a positive mindset and improve their overall quality of life.
Surgery as a Last Resort for Celiac Disease Treatment
In rare cases, surgery may be necessary for individuals with celiac disease who do not respond to other treatment options or who develop complications such as strictures or perforations in the small intestine.
Surgical options for celiac disease include stricturoplasty, which involves widening narrowed areas of the intestine, and resection, which involves removing damaged sections of the intestine. These surgeries are typically performed by a gastroenterologist or a surgeon specializing in gastrointestinal disorders.
While surgery can provide relief for some individuals with celiac disease, it is important to note that it is considered a last resort and is not a cure for the condition. Following surgery, individuals will still need to adhere to a strict gluten-free diet to prevent further damage to the small intestine.
Future Trends in Celiac Disease Treatment Research
Research into celiac disease treatment is ongoing, and there are several promising new treatments on the horizon. One area of research focuses on developing medications that can break down gluten in the digestive system, making it less harmful for individuals with celiac disease.
Another area of research explores the use of enzymes that can be taken orally to help digest gluten. These enzymes may help individuals with celiac disease tolerate small amounts of gluten without experiencing symptoms or damage to the small intestine.
There is also ongoing research into vaccines that can desensitize the immune system to gluten, reducing the immune response and preventing damage to the small intestine. These vaccines may one day provide a long-term solution for individuals with celiac disease.
Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder that requires lifelong management. While there is currently no cure for celiac disease, there are several treatment options available to help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Medications can be used to control inflammation and suppress the immune response, but they are not without their drawbacks. The most effective treatment for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet, which allows the small intestine to heal and reduces inflammation. Nutritional supplements may also be necessary to address nutrient deficiencies common in individuals with celiac disease.
In addition to medication and diet, alternative therapies, lifestyle changes, regular medical checkups, psychological support, and surgery may be necessary for some individuals with celiac disease. Ongoing research into celiac disease treatment is promising, with new medications and therapies on the horizon.
It is important for individuals with celiac disease to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. With the right treatment and support, individuals with celiac disease can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
If you’re looking for more information on celiac disease treatment options, you may also be interested in reading about the benefits of probiotics for celiac disease. Probiotics have been shown to help improve gut health and reduce inflammation, which can be beneficial for individuals with celiac disease. To learn more about the top 10 best probiotics for celiac disease, check out this informative article: https://turntobehealthy.com/top-10-best-probiotics-for-celiac-disease/.
FAQs
What is celiac disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine. It is triggered by the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
What are the symptoms of celiac disease?
Symptoms of celiac disease can vary widely and may include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, and weight loss.
How is celiac disease diagnosed?
Celiac disease is typically diagnosed through blood tests and a biopsy of the small intestine.
What are the treatment options for celiac disease?
The primary treatment for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet. In addition, medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms and promote healing of the small intestine.
What medications are used to treat celiac disease?
Medications used to treat celiac disease include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologic therapies.
What lifestyle changes can help manage celiac disease?
In addition to following a gluten-free diet, lifestyle changes that can help manage celiac disease include regular exercise, stress management, and getting enough sleep.
Is there a cure for celiac disease?
There is currently no cure for celiac disease. However, following a strict gluten-free diet can effectively manage symptoms and prevent complications.