Celiac Disease and Pregnancy: Risks and Management

Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine and is triggered by the consumption of gluten. It is estimated that 1 in 100 people worldwide have celiac disease, and it can have a significant impact on various aspects of a person’s life, including fertility and pregnancy. Understanding the link between celiac disease and fertility is crucial for women who are planning to conceive or are already pregnant. By managing their condition effectively, women with celiac disease can increase their chances of having a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that damages the small intestine and can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss.
- Women with celiac disease may have difficulty getting pregnant and may be at increased risk for complications during pregnancy, such as miscarriage and preterm birth.
- Babies born to women with untreated celiac disease may be at increased risk for low birth weight, growth problems, and developmental delays.
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as iron and folic acid, are common in women with celiac disease and can affect both maternal and fetal health.
- Following a strict gluten-free diet during pregnancy can help reduce the risk of complications and ensure optimal health for both mother and baby.
Understanding Celiac Disease: Symptoms and Diagnosis
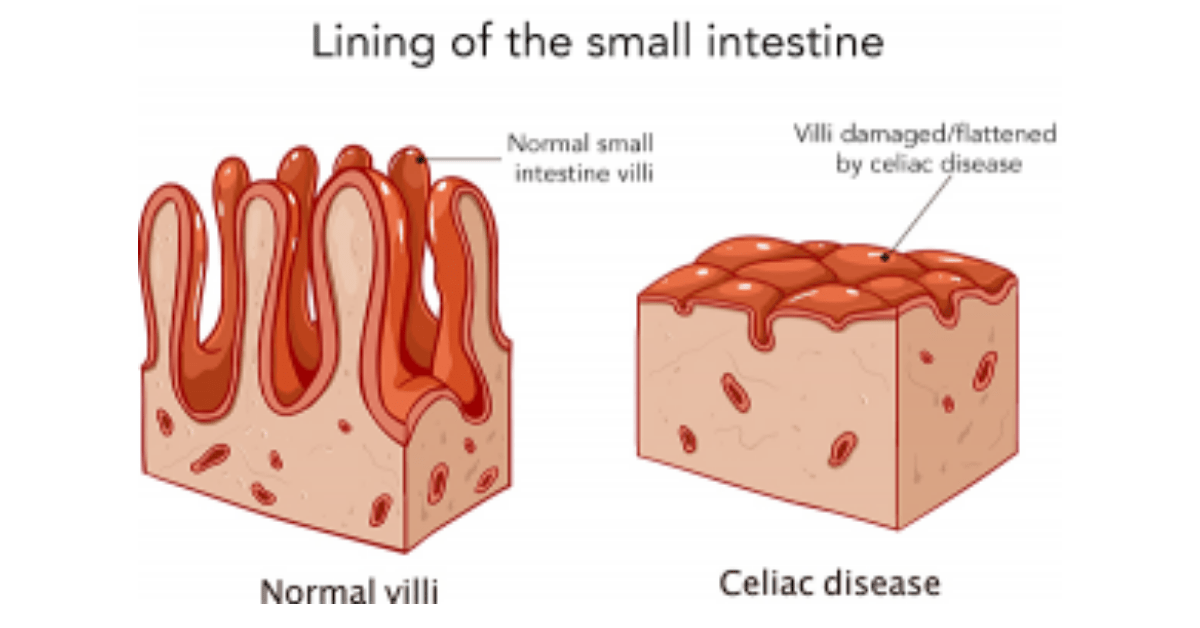
Celiac disease is characterized by an immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When someone with celiac disease consumes gluten, their immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine, leading to inflammation and damage. This damage can cause a wide range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, fatigue, and weight loss.
Diagnosing celiac disease can be challenging because the symptoms can vary widely from person to person. In some cases, individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms at all. The diagnostic process typically involves a combination of blood tests to check for specific antibodies associated with celiac disease and an intestinal biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
The Link between Celiac Disease and Fertility
Research has shown that there is a link between celiac disease and fertility issues in both men and women. In women, celiac disease can lead to hormonal imbalances that disrupt the menstrual cycle and make it more difficult to conceive. Additionally, the inflammation caused by celiac disease can affect the health of the reproductive organs.
In men, celiac disease can also lead to hormonal imbalances that affect sperm production and quality. This can result in reduced fertility or even infertility. It is important for both men and women with celiac disease who are trying to conceive to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively and increase their chances of successful conception.
Pregnancy Risks for Women with Celiac Disease
Pregnancy can pose additional risks for women with celiac disease. The inflammation and damage to the small intestine caused by celiac disease can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients, which are crucial for a healthy pregnancy. This can lead to complications such as anemia, low birth weight, and developmental delays in the baby.
Women with celiac disease also have an increased risk of miscarriage and preterm birth. The exact reasons for these increased risks are not fully understood, but it is believed that the inflammation and immune response triggered by celiac disease may play a role.
Potential Complications for the Baby
Babies born to mothers with celiac disease may also be at risk for certain complications. The malabsorption of nutrients caused by celiac disease can result in nutrient deficiencies in the mother, which can affect the baby’s development. This can lead to low birth weight and an increased risk of developmental delays.
Additionally, if a mother with celiac disease continues to consume gluten during breastfeeding, it is possible that the gluten proteins could pass into breast milk and potentially cause a reaction in the baby. It is important for women with celiac disease to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the best approach to breastfeeding and ensure that their baby is not exposed to gluten.
Nutritional Deficiencies in Celiac Disease and Pregnancy

One of the key challenges for women with celiac disease during pregnancy is managing nutritional deficiencies. The inflammation and damage to the small intestine can interfere with the absorption of important nutrients such as iron, folic acid, calcium, and vitamin D. These nutrients are crucial for a healthy pregnancy and the development of the baby.
It is important for women with celiac disease to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their nutrient levels and ensure that they are getting the necessary nutrients through their diet or supplements. A registered dietitian who specializes in celiac disease can provide guidance on how to maintain a balanced and nutritious diet while avoiding gluten.
Gluten-Free Diet during Pregnancy: Benefits and Challenges
A gluten-free diet is the only treatment for celiac disease, and it is essential for women with celiac disease to follow this diet during pregnancy to minimize the risks to themselves and their baby. A gluten-free diet involves avoiding all sources of gluten, including wheat, barley, rye, and any products that contain these grains.
Following a gluten-free diet during pregnancy can have several benefits. It can help reduce inflammation in the body, improve nutrient absorption, and minimize the risk of complications such as miscarriage and preterm birth. However, maintaining a gluten-free diet can be challenging, as gluten is found in many common foods and ingredients.
Managing Celiac Disease during Pregnancy: Tips and Strategies
Managing celiac disease during pregnancy requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some tips and strategies for women with celiac disease:
1. Work closely with a healthcare provider: It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider who has experience in managing celiac disease during pregnancy. They can provide guidance on diet, monitor nutrient levels, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
2. Follow a strict gluten-free diet: It is crucial to strictly adhere to a gluten-free diet during pregnancy. This means avoiding all sources of gluten, including hidden sources such as sauces, dressings, and processed foods.
3. Read labels carefully: When shopping for food, it is important to read labels carefully to ensure that products are gluten-free. Look for products that are certified gluten-free or labeled as “gluten-free” to minimize the risk of cross-contamination.
4. Plan meals and snacks ahead of time: Planning meals and snacks ahead of time can help ensure that you have gluten-free options available and reduce the risk of accidental gluten exposure.
5. Educate yourself and others: It is important to educate yourself about celiac disease and the gluten-free diet, as well as educate others who may be involved in your care, such as family members, friends, and healthcare providers.
Importance of Prenatal Care for Women with Celiac Disease
Prenatal care is crucial for all pregnant women, but it is especially important for women with celiac disease. Regular prenatal check-ups can help monitor the health of both the mother and the baby and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
During prenatal visits, healthcare providers will monitor the mother’s nutrient levels, check for any signs of complications, and provide guidance on managing celiac disease during pregnancy. They may also recommend additional tests or screenings to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Breastfeeding and Celiac Disease: Considerations and Recommendations
Breastfeeding is generally recommended for all babies, including those born to mothers with celiac disease. Breast milk provides essential nutrients and antibodies that can help support the baby’s immune system and overall development.
However, there are some considerations and recommendations for breastfeeding for women with celiac disease. If a mother continues to consume gluten while breastfeeding, it is possible that the gluten proteins could pass into breast milk and potentially cause a reaction in the baby. It is important for women with celiac disease to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the best approach to breastfeeding and ensure that their baby is not exposed to gluten.
Postpartum Care for Women with Celiac Disease: What to Expect
After giving birth, women with celiac disease may require additional postpartum care to ensure that their condition is properly managed. This may include monitoring nutrient levels, managing any ongoing symptoms or complications, and adjusting the gluten-free diet as needed.
It is important for women with celiac disease to continue working closely with their healthcare providers during the postpartum period to address any concerns or complications that may arise. Regular follow-up appointments can help ensure that the mother’s health and well-being are being properly monitored and that any necessary adjustments to the management plan are made.
Understanding celiac disease and its impact on pregnancy is crucial for women with this condition. By managing their celiac disease effectively, women can increase their chances of having a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby. It is important for women with celiac disease to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a management plan for pregnancy and beyond. By following a strict gluten-free diet, monitoring nutrient levels, and seeking regular prenatal and postpartum care, women with celiac disease can minimize the risks and complications associated with pregnancy and ensure the best possible outcomes for themselves and their babies.
If you’re interested in learning more about the health benefits of vitamin A, you may want to check out this informative article on TurnToBeHealthy.com. However, if you’re specifically looking for information on Celiac Disease and Pregnancy: Risks and Management, I recommend reading this related article. It provides valuable insights and guidance for women with celiac disease who are planning to conceive or are already pregnant. Understanding the risks and implementing proper management strategies is crucial for a healthy pregnancy.
FAQs
What is celiac disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine. It is triggered by the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
What are the risks of celiac disease during pregnancy?
Untreated celiac disease during pregnancy can lead to complications such as miscarriage, preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth. It can also increase the risk of maternal anemia, gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia.
How is celiac disease diagnosed during pregnancy?
Celiac disease can be diagnosed through blood tests that measure the levels of certain antibodies. A biopsy of the small intestine may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the treatment for celiac disease during pregnancy?
The only treatment for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet. This can be challenging during pregnancy, but it is essential to ensure the health of both the mother and the baby.
What are the dietary restrictions for pregnant women with celiac disease?
Pregnant women with celiac disease must avoid all foods that contain gluten, including wheat, barley, rye, and some oats. They should also be careful to avoid cross-contamination in the kitchen and when eating out.
Can celiac disease affect breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding is generally safe for women with celiac disease, as long as they continue to follow a strict gluten-free diet. However, some babies may be sensitive to gluten and may need to be monitored for symptoms.
What are the long-term effects of celiac disease on pregnancy?
If celiac disease is left untreated, it can lead to long-term complications such as infertility, osteoporosis, and an increased risk of certain cancers. It is important to manage the condition during pregnancy to prevent these complications.